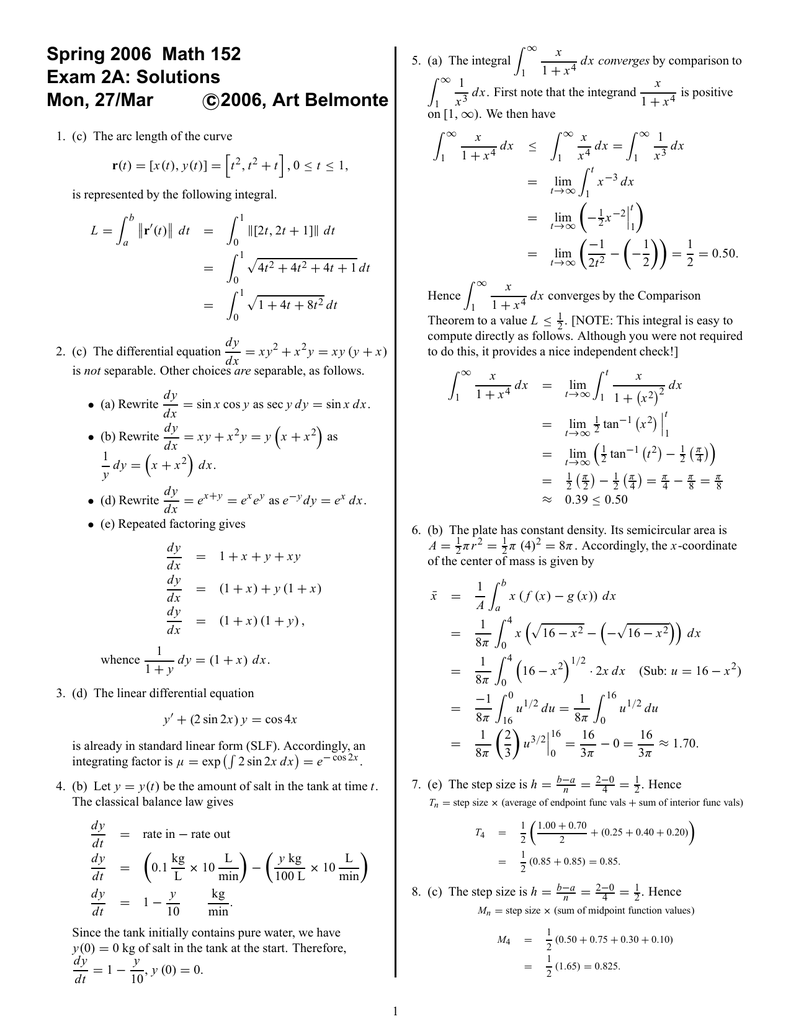
· Calculus is the association of change in one variable with respect to another So dy/dx literally means how the variable y changes as x changes Imagine a graph, draw the line y = 1 It doesn't matter what value of x you look at, y = 1 It x changes, decreases or increaes, y will always be 1Dy/dx=(xy1)^2(1) Let xy1=t 1dy/dx=dt/dx dy/dx=dt/dx 1(2) from eqn(1) & (2) dt/dx1=t^2 dt/dx=1t^2 1dt/(1t^2)=dx tan^1(t)=xC t=tanDy/dx P(x)y=Q(x) So we compute and integrating factor, I, using;

Ipe Material Notes
Y/x dy/dx=(1 x^2)^-1/2(1 y^2)^1/2
Y/x dy/dx=(1 x^2)^-1/2(1 y^2)^1/2-Solve y(dy/dx) x = (1/2)((x2 y2)/x)2 Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to get solutions to their queriesF y F dx dy y x 1 cos 1 H c c y f(x) F F (x,y) 0 x Rn F n 1 设 n 1 元函数 F 在点 ( , , , 0) (0) P 0 x 1 x n y 的某邻域 O (P 0,r) 上有 定义,而且 ( , , , 0) 0 (0) F x 1 x n y 在 O (P 0,r)



If Y Log 1 X 2 1 X 2 Then Dy Dx A 4x 3 1 X 4
See the answer Differential Equations Problem Part C / D Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (3 ratings) Previous question Next question · Solve the differential equation dy/dx = 1 x y^2 xy^2, when y = 0, x = 0 asked Sep 21, in Differential Equations by Chandan01 ( 512k points) differential equationsIf x(1y)^1/2y(1x)^1/2=0 then prove that dy/dx =1/(1x)^2 Maths Continuity and Differentiability
· This is separable 1 1 y dy dx = x2 ∫ 1 1 y dy dx dx = ∫ x2 dx ∫ 1 1 y dy = ∫ x2 dx ln(1 y) = x3 3 C 1 y = ex3 3 C = ex3 3 eC = Cex3 3 y = Cex3 3 −1 Applying the IV 3 = Ce0 −1 = C −1 ⇒ C = 4Integrate x^2 sin y dx dy, x=0 to 1, y=0 to pi;Answer to Solve the initial value problem dy/dx = (y^2 1)/(x^2 1), y(2) = 2 By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to
Find dy/dx for (x^2) (y^3) ln (x^y) = 5sin (6x)/x^ (1/2) To differentiate this equation we must use the implicit method, looking at the left side of the equation, to find the differential of the first term we must use the product rule, therefore the differential of x 2 y 3 is 2xy 3 (x 2 3y 2 ) (dy/dx)Find dy/dx y^2=(x1)/(x1) Differentiate both sides of the equation Differentiate the left side of the equation Tap for more steps Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that is where and Tap for more steps To apply the Chain Rule, set asIntegrate x/(x1) integrate x sin(x^2) integrate x sqrt(1sqrt(x)) integrate x/(x1)^3 from 0 to infinity;



Ipe Material Notes
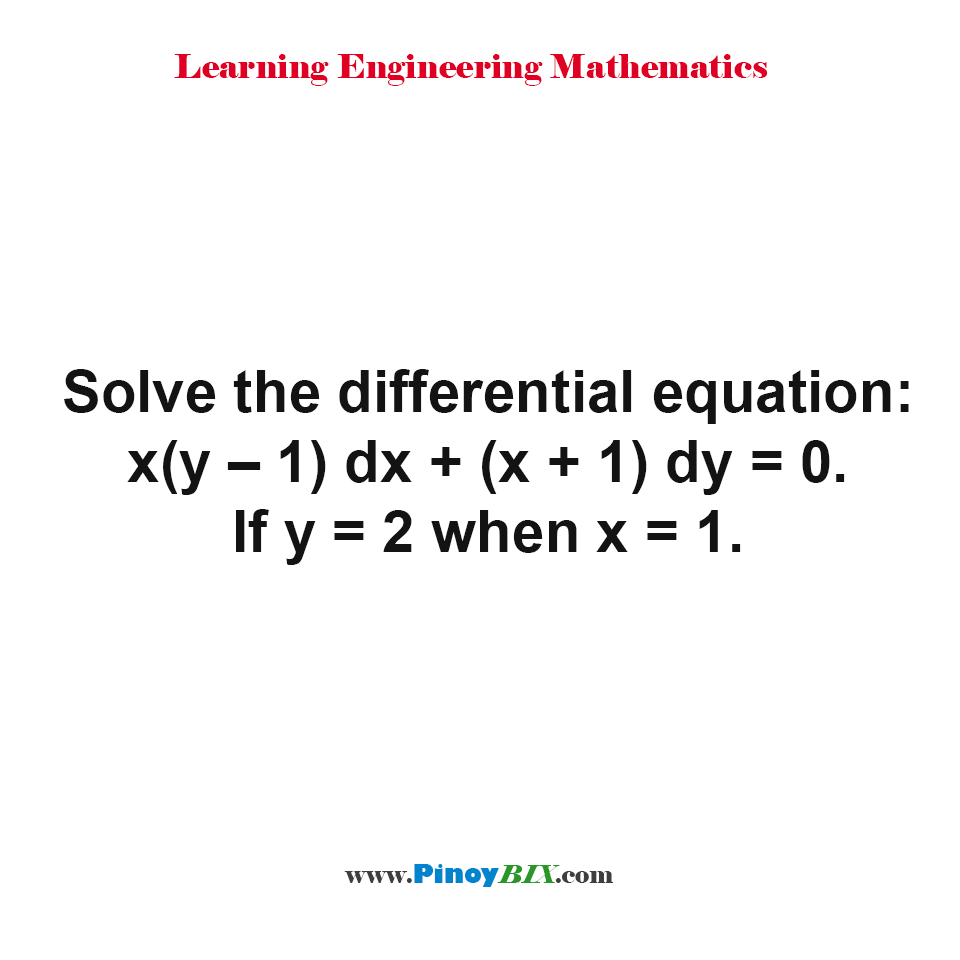


Solution Solve The Differential Equation X Y 1 Dx X 1 Dy 0 If Y 2 When X 1
WBJEE 15 8 If √y = cos − 1x, then it satisfies the differential equation (1 − x2) − xdy dx = c, where c is equal to WBJEE 14 9 The curve y = (cosx y)1 / 2 satisfies the differential equation WBJEE 14 10 A solution of the differential equation (dy dx)2 − xdy dx y = 0 is · Solve the differential equation dy/dx = (1 y 2)/(1 x 2) bseb model set; · The solution of x^3(dy/dx) 4x^2 ∙ tany = e^x ∙ secy satisfying y(1) = 0 is asked Apr 18, 19 in Mathematics by Ankitk ( 741k points) differential equations



How Do You Find Dy Dx For Y 2x Sqrt X 1 Socratic



Solve Y 1 Xy Dx X 1 Xy X 2y 2 Dy 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange
· xdy/dx = y 2 (xy)^1/2 Divide both sides by x and get dy/dx = y/x 2 (xy)^1/2/x →dy/dx = y/x 2 (y/x)^1/2 Let y=Vx or V=y/x → dy/dx= VxdV/dx after substitution dy/dx = y/x 2 (xy)^1/2/x becomes VxdV/dx =V2V^1/2 ie xdV/dx =2V^1/2Simple and best practice solution for (x^2)dxy(x1)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve itSimple and best practice solution for (x^2)dyy(1x)dx=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework



Engineering Mathematics Notes



Ejercicios De Calculo Vectorial Pagina 2 Monografias Com
Weekly Subscription $199 USD per week until cancelled Monthly Subscription $699 USD per month until cancelled Annual Subscription $2999 USD per year until cancelledCalculus Applications of Definite Integrals Solving Separable Differential Equations 1 Answer Eddie Jul 11, 16 # y = xtan (ln x C)# Explanation This is a first order linear homogeneous equation NB here homogeneousView Jean 2docx from MATH DIFFERENTI at Bulacan State University, Malolos 2 xdy − y ( x 1 ) dx 6 y 3 dx=0 ¿ 1 1 2 xdy − y ( x 1 ) 6 y 3=0 2 xdx dx dy y ( x 1 ) − 6 y 3=0 dx 2x dy
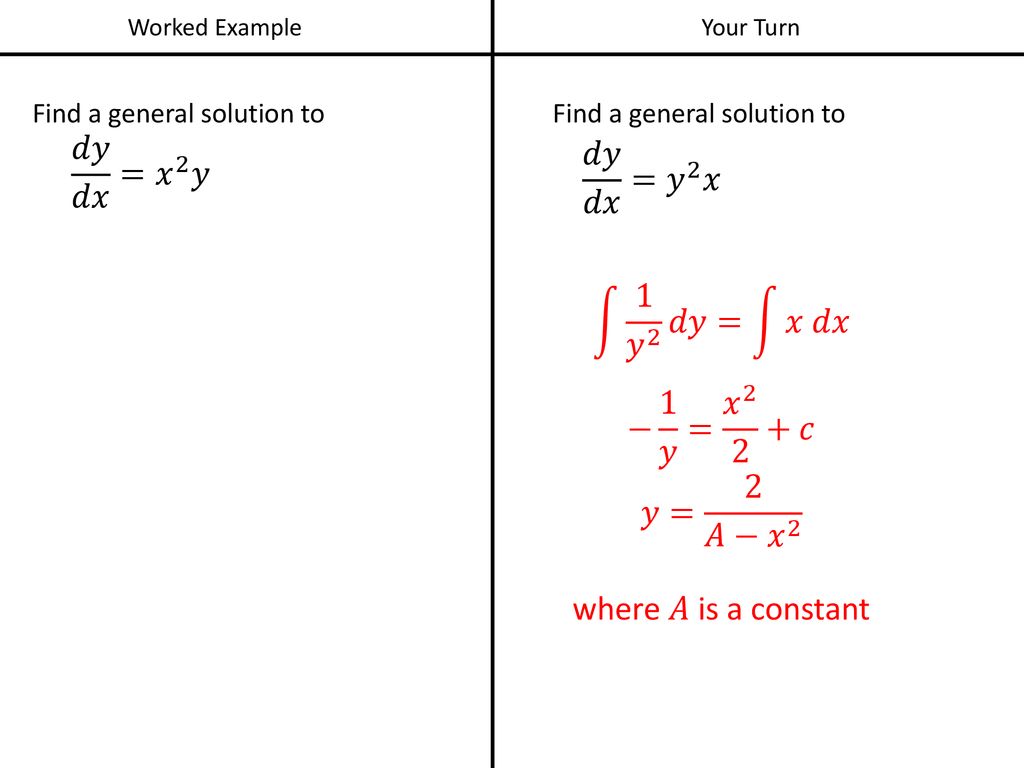


Differential Equations Separation Of Variables Ppt Download



Calc3 1001 By James Bardo Issuu
This is separable Divide both sides by x(1 — y) to put all factors with x on the left and all factors with y on the right (1 — x^2)/x dx = y(1 y)/ (1 — y) dy Now integrate both sides You'll need to use polynomial division to rewrite both sides as a polynomial plus a proper rational expression firstWeekly Subscription $199 USD per week until cancelled Monthly Subscription $699 USD per month until cancelled Annual Subscription $2999 USD per year until cancelledThis is almost certainly a problem in a section of the text on "exact" equations, ie ones of the form dF= F,x dx F,y dy =0 The solution is F(x,y)=constant You need to look for an integrating factor A such that F,x = A 2 x y F,y = A (x^2 y^2


Solved Solve The Following Bernoulli Equations B 2 X 2 Dy Dx Xy X 3 Y 3 C Y X Y X2 5 X 2 Y 1 2 D X Dy Dx 6y 3xy Course Hero



Misc 6 Find General Solution Dy Dx Root 1 Y2 1 X2 0
Free Multivariable Calculus calculator calculate multivariable limits, integrals, gradients and much more stepbystepI = e^(int P(x) dx) \ \ = exp(int \ (12x)/x^2 \ dx) \ \ = exp( 2lnx 1/x ) \ \ = e^( lnx^2 1/x ) \ \ = e^( lnx^2)e^( 1/x ) \ \ = 1/x^2e^( 1/xClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If y = tan^1 ( 2x/1 x^2 ) , then find dy/dx



Problemario De Ecuaciones Diferenciales By Gerson Villa Gonzalez Issuu



X 1 X 2 Dy 2x 2y Y Ax 3 Dx 0
Simple and best practice solution for (y^2xy1)dx(x^2xy1)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve it43 Solve x 3xy = 0 In this type of equations, having more than one variable (unknown), you have to specify for which variable you want the equation solved We shall not handle this type of equations at this timeShare It On Facebook Twitter Email 1 Answer 1 vote answered Feb 7, by KumariMuskan (339k points) selected Feb 11, by Nakul01 Best answer Given



If Y X 1 X Show That X 2 Dy Dx Xy 2 0



El Blog De Jair Beltran Ecuaciones Diferenciales Variables Separables Cambio De Variable Ecuaciones Diferenciales Exactas
I assume you're after a particular solution to the differential equation In which case I'll proceed with separation of variables The equation can be manipulated algebraically math\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{x^{2}y}{(1x^{3})}/math Without loss of gSimplifying dx = 0 The solution to this equation could not be determined This subproblem is being ignored because a solution could not be determined Subproblem 2 Set the factor '(y 2 x 2)' equal to zero and attempt to solve Simplifying y 2 x 2 = 0 Reorder the terms x 2 y 2 = 0 Solving x 2 y 2 = 0 Move all terms containing d to theCalculus Find dy/dx y=1/ (x^2) y = 1 x2 y = 1 x 2 Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx ( 1 x2) d d x ( y) = d d x ( 1 x 2) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate the right side of the equation Tap for more steps



Solve 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 X Dy Dx Y X 1 X 2 3 2 Mathematics 2 Question Answer Collection
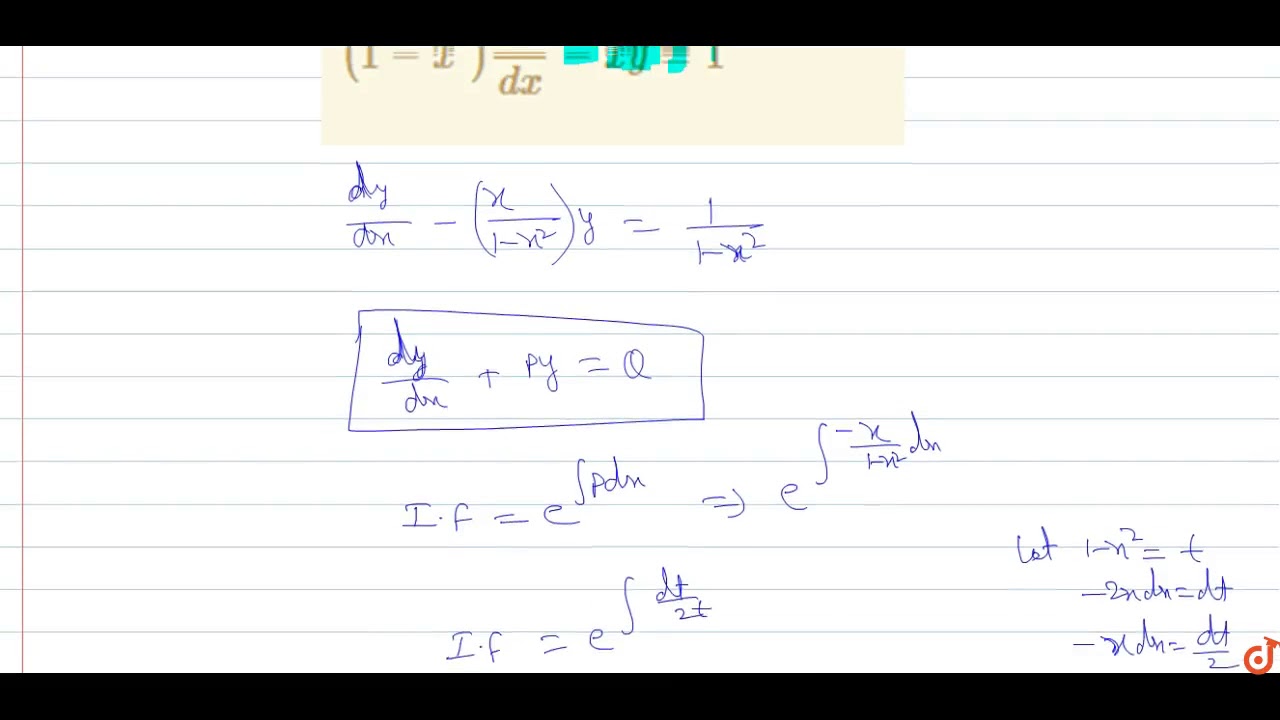


1 X 2 Dy Dx Xy 1 Youtube
View more examples » Access instant learning tools Get immediate feedback and guidance with stepbystep solutions and Wolfram Problem Generator LearnIntegrate 1/(cos(x)2) from 0 to 2pi; · dy/dx = y^2 x^2 /2xy (i) this is a homogeneous equation put y = vx dy/dx = v x dv/dx(ii) from (i) and (ii) v x dv/dx = {v^2 x^2 x^}/ 2vx^2



Example 9 Find General Solution Of Dy Dx X 1 2 Y Examples
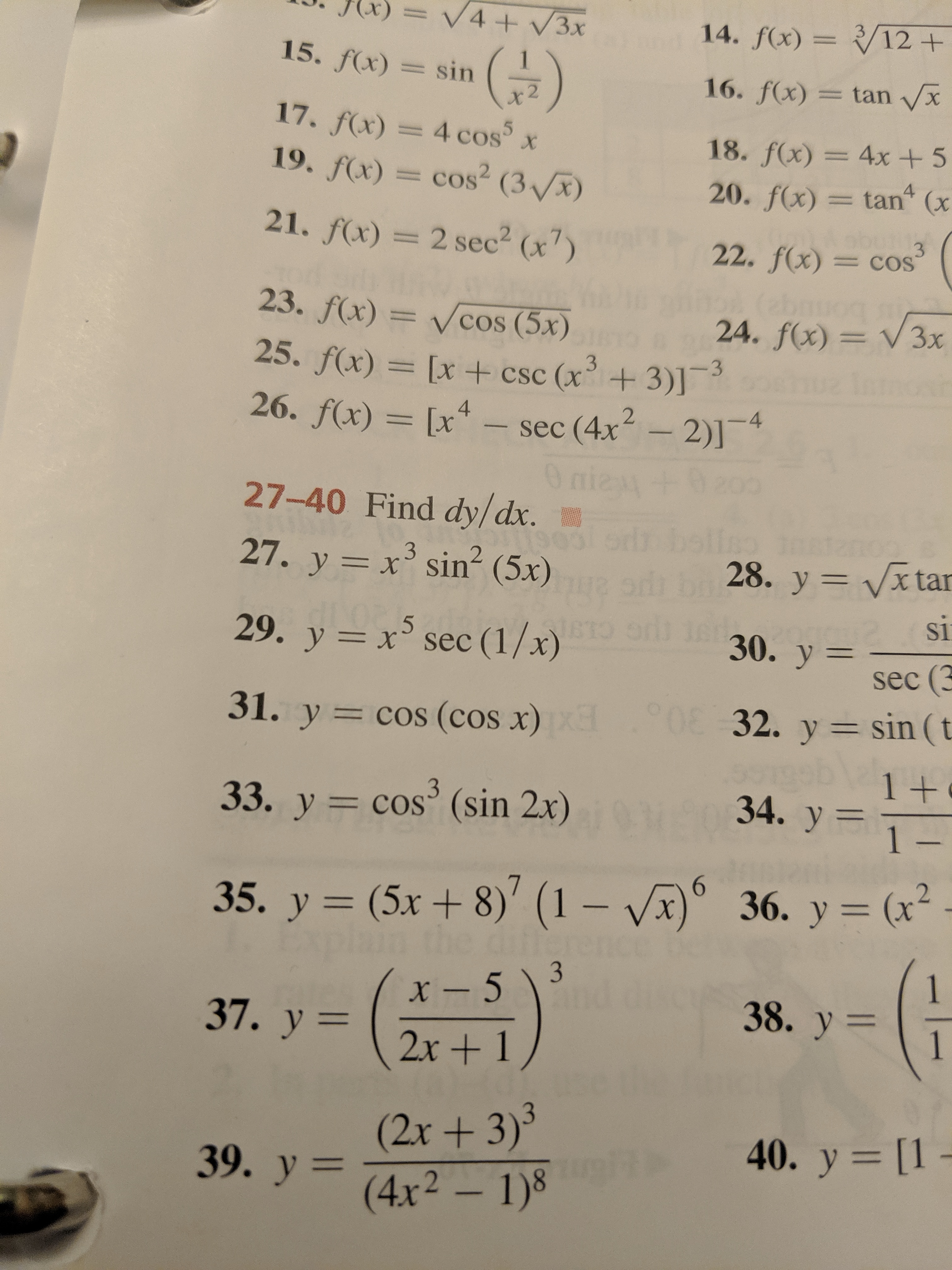


Answered V4 3x 14 F X 12 15 F X Sin 16 Bartleby
Calculus Find dy/dx y^2=1/ (1x^2) y2 = 1 1 − x2 y 2 = 1 1 x 2 Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y2) = d dx ( 1 1−x2) d d x ( y 2) = d d x ( 1 1 x 2) Differentiate the left side of the equation Tap for more stepsMove the terms of the y variable to the left side, and the terms of the x variable to the right side Integrate both sides of the differential equation, the left side with respect to y, and the right side with respect to x Solve the integral \int\frac {1} {y^2}dy and replace the result in the differential equation Divide x^2 by 1xAnswer to Evaluate (x2 y2) 1 / 2 dy dx Draw the region set up the integral in polar coordinates Evaluate By signing up, you'll get thousands of



Worked Example Implicit Differentiation Video Khan Academy



工數作業1 Hhh Engineering Mathematics Studocu
· y = x^2(1 e^( 1/x1 )) We have dy/dx (12x)/x^2y = 1 and y(1)=0 We can use an integrating factor when we have a First Order Linear nonhomogeneous Ordinary Differential Equation of the form; · What is a solution to the differential equation #dy/dx=y^2/x^2y/x1#? · Let y = y(x) be the solution curve of the differential equation, (y^2 x)dy/dx = 1, satisfying y(0) = 1 asked Jan 21, in Mathematics by Pankaj01 ( 502k points) jee main



Math 432 Hw 2 4 Solutions



If Y Log 1 X 2 1 X 2 Then Dy Dx A 4x 3 1 X 4
Question Differential Equations Problem Solve Dy/dx = 1/x^2 1 For Y (0) = 0 Solve Y' = Y^3 For Y (0) = 1 This problem has been solved!Again this a first order Linear DE of the form dy/dx Py = Q, where P ad Q ae both functions of x Let us find the Integrating Factor as follows


Document



Example 10 Find General Solution Dy Dx 1 Y2 1 X2 Examples



The Solution Of Dy Dx 2x 1 X 2 Y 1 1 X 2 2
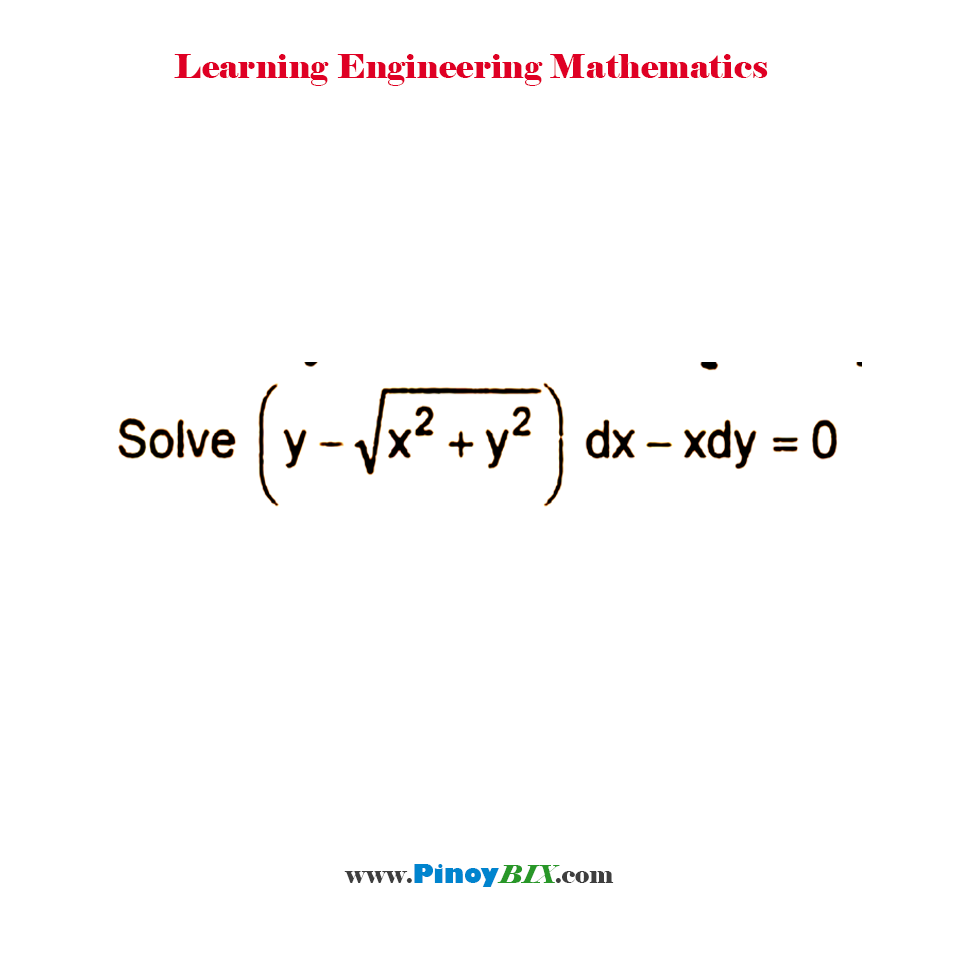


Solution Solve Y X 2 Y 2 Dx Xdy 0



Misc 14 Find Particular Solution X 1 Dy Dx 2e Y 1



Ex 9 4 12 Find Particular Solution X X2 1 Dy Dx 1 Y 0



Example 28 Solve Differential Equation Dx Dy X 1 Y 2 Tan 1 Y 1



Y Log X Root 1 X2 Prove That 1 X2 D2y Dx2 X Dy Dx 0 Brainly In



Ex 9 4 6 Find General Solution Dy Dx 1 X2 1 Y2



Solve 1 X Dydx Xy 1 X
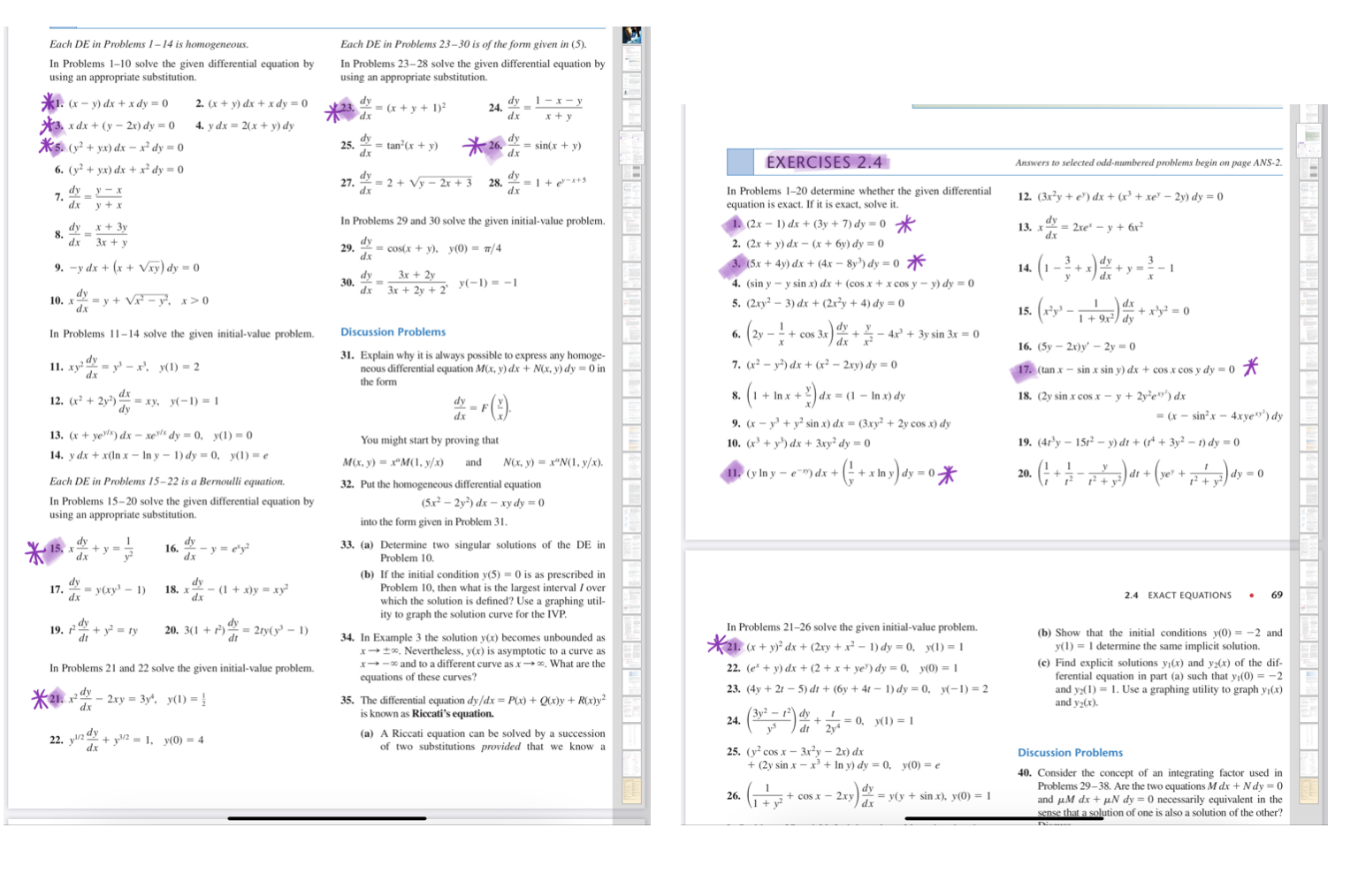


Solved Each De In Problems 1 14 Is Homogeneous In Proble Chegg Com



If X 1 Y Y 1 X 0 Then Prove That 1 X 2 Dydx 1 0
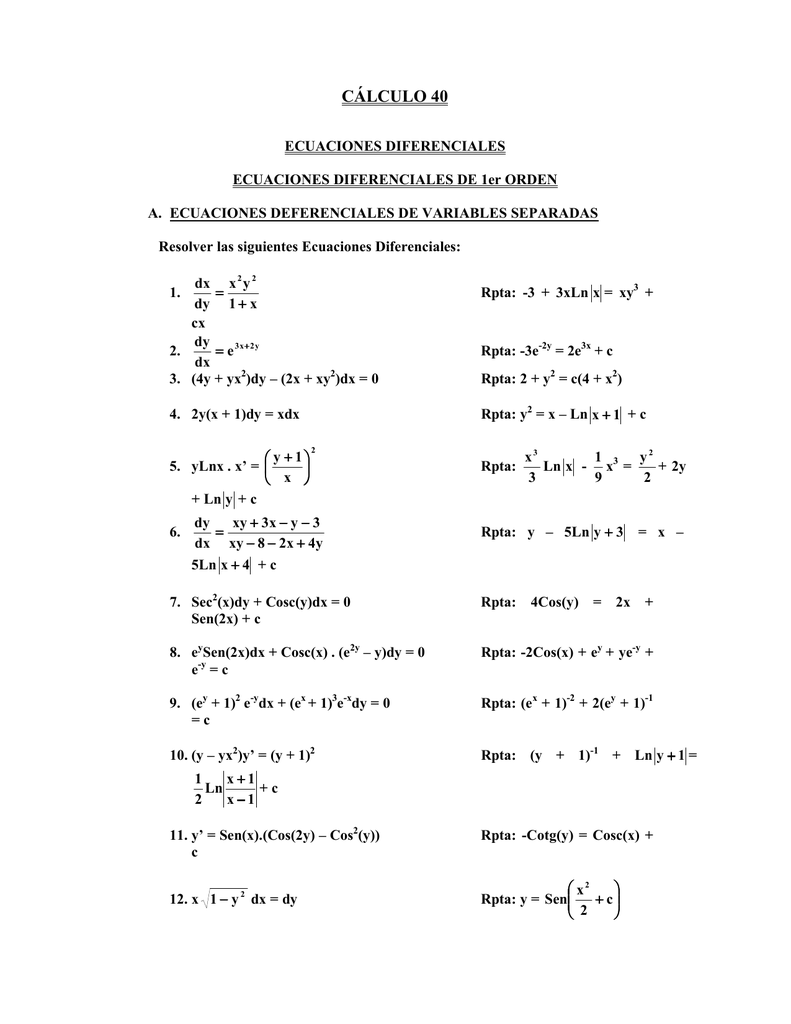


Calculo 40 Web Del Profesor


Differential Equations Separation Of Variables Ppt Download


How To Solve This Equation X Y 3 Dx 3x Y 1 Dy 0 Quora



If 1 X 2 1 Y 2 A X Y Then Prove That Dy Dx



If Y Sin 2tan 1 1 X 1 X 1 2 Then Find Dy Dx And If 5 X 5 Y 5 X Y Then Prove That Dy Dx 5 Y X 0 Mathematics Topperlearning Com Q011rcnn



X Y 1 Dx Y X 1 Dy 0find The General Solution Of The Differential Equation Brainly In


Differential Equations Separation Of Variables Ppt Download



If Y Log X Root X2 1 Then Prove That X2 1 Dy Dx X Dy Dx 0 Brainly In



Engineering Mathematics Notes



Misc 7 Show That General Solution Is X Y 1 A 1 X Y 2xy



Solve The Differential Equation 1 X 2 1 Y Dx Xy 1 Y Dy Brainly In


How To Solve 2x Y 1 Dx X 4y 3 Dy 0 Quora
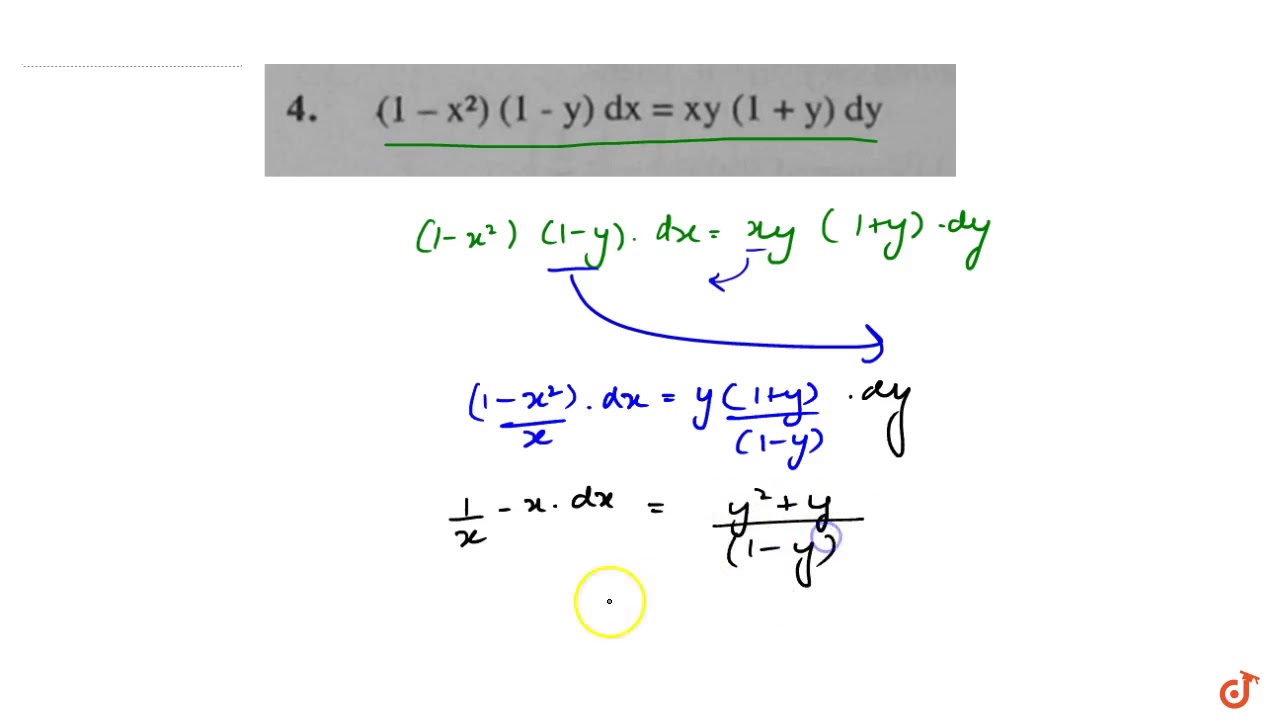


1 X 2 1 Y Dx X Y 1 Y Dy Y 4 1 X 1 Y Dx Xy 1 Y Dy Youtube


What Is The Solution Of Differential Equation D 2y Dx 2 2 Dy Dx Y 0 When X 0 Y 1 Dy Dx 2 Quora



Solve The Differential Equation Frac Dy Dx Frac Y Sin X Tan Frac 1 2 X Mathematics Stack Exchange



Engineering Mathematics Notes



Differential Equatio Long Answer Questions 7 M R Solye 2x Y 3 Dx



Lesson 6 Exact Equations Determine Whether Or Not Each Of



Engineering Mathematics Notes



Q 5 Consider The Differential Equation X Dy X Ydx Y Xy Math
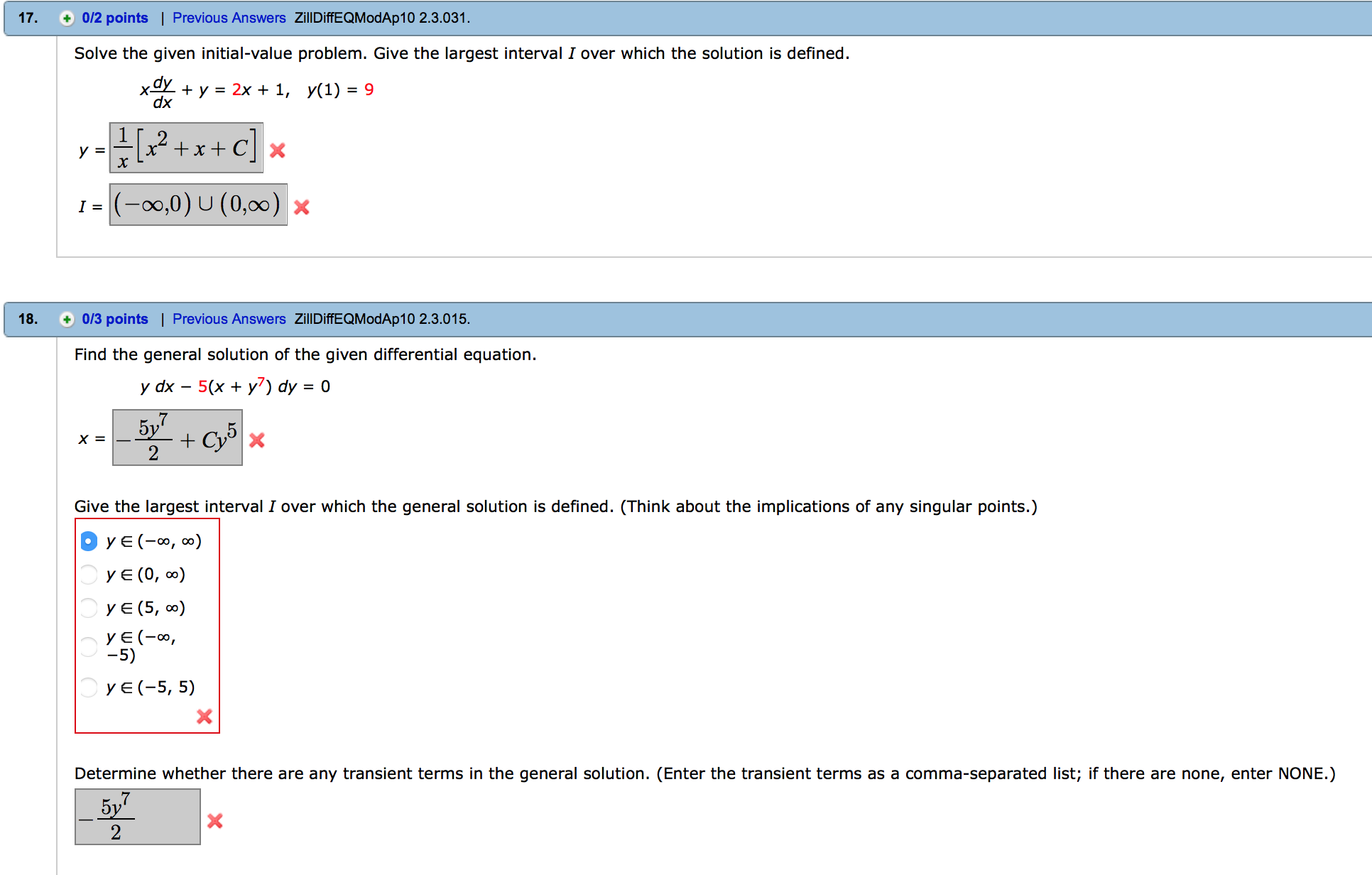


Solved Solve The Given Initial Value Problem Give The La Chegg Com



Engineering Mathematics Notes



Ordinary Differential Equations Methods Of Numerical Analysis Assignment Docsity



Prove That Frac Dy Dx Frac1 1 X 2 For Given That X Sqrt 1 Y Y Sqrt 1 X 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange



Engineering Mathematics Notes



If 1 X 6 1 2 1 Y 6 1 2 A X 3 Y 3 The Prove That Dy Dx X 2 Y Askiitians



Engineering Mathematics Notes
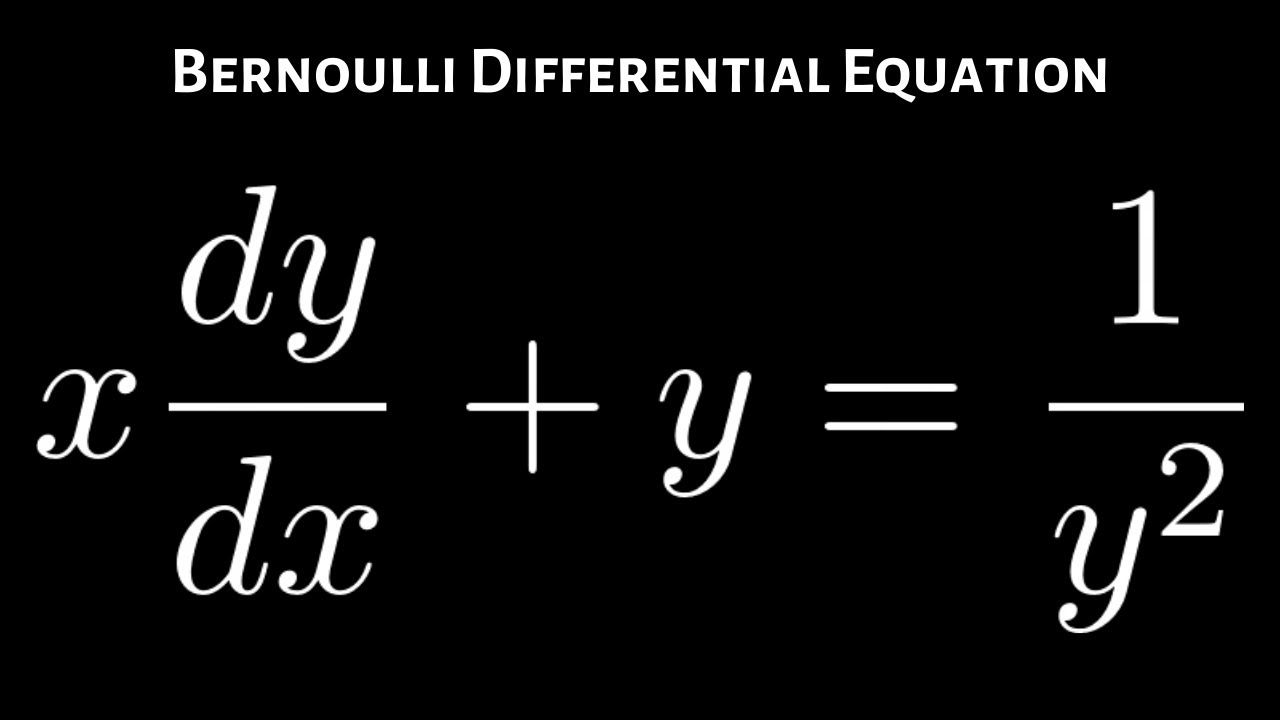


Bernoulli Differential Equation X Dy Dx Y 1 Y 2 Youtube


Engineering Mathematics Ii Ma Ppt Download



Solved The Given Differential Equations Are Linear Or Non Chegg Com



Solution Of The Differential Equation 1 Y 2 X E Tan 1 Y Dy Dx 0 Youtube



Solved First Check That The Ode S Are Exact Then Find An Chegg Com



Solve 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 X Dy Dx Y X 1 X 2 3 2 Mathematics 2 Question Answer Collection



Math 432 Hw 2 5 Solutions Pdf Free Download



Solve X Dy Dx Y X 1 Ex Brainly In



Math 432 Hw 2 5 Solutions Pdf Free Download



If X2 Y2 Z2 2xyz 1 Then Dx 1 X2 1 2 Dy 1 Y2 1 2 Dz 1 Z2 1 2 Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com
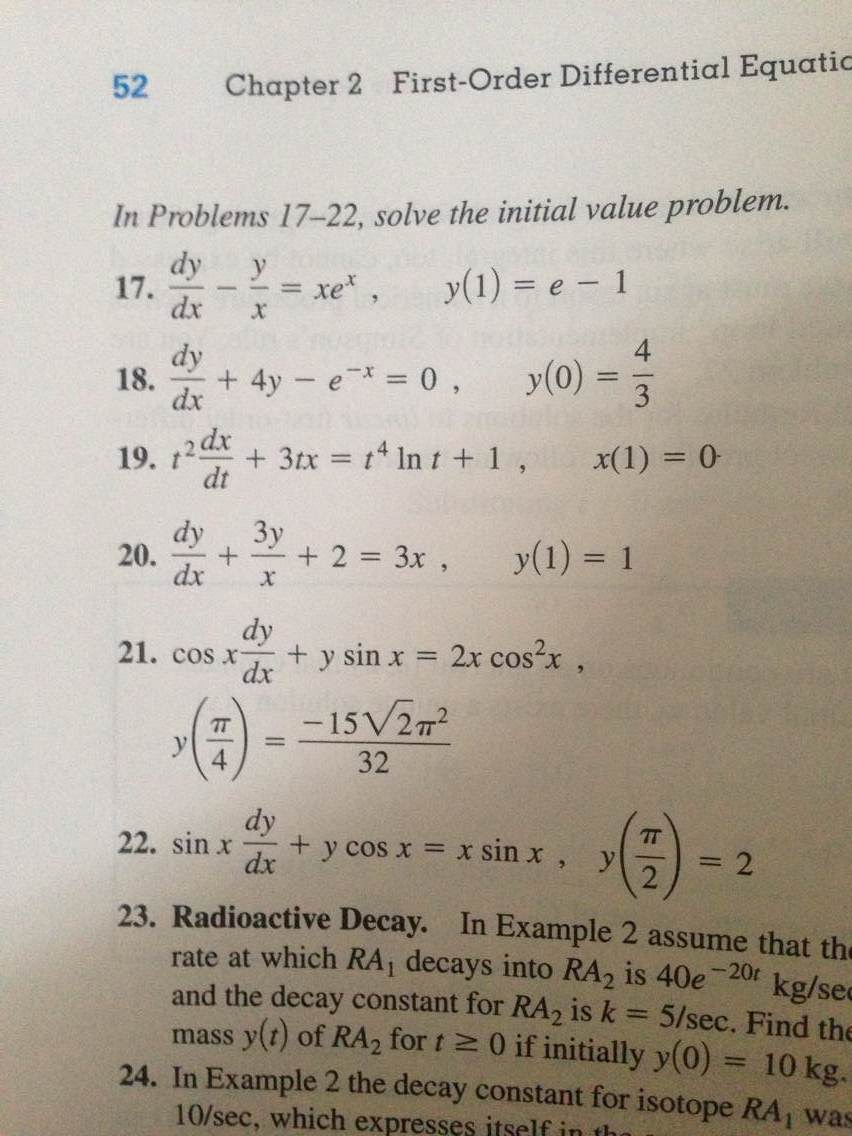


Solved In Problems 17 22 Solve The Initial Value Problem Chegg Com



Unit 03 Differential Equations Doc Logical Truth Equations


Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy
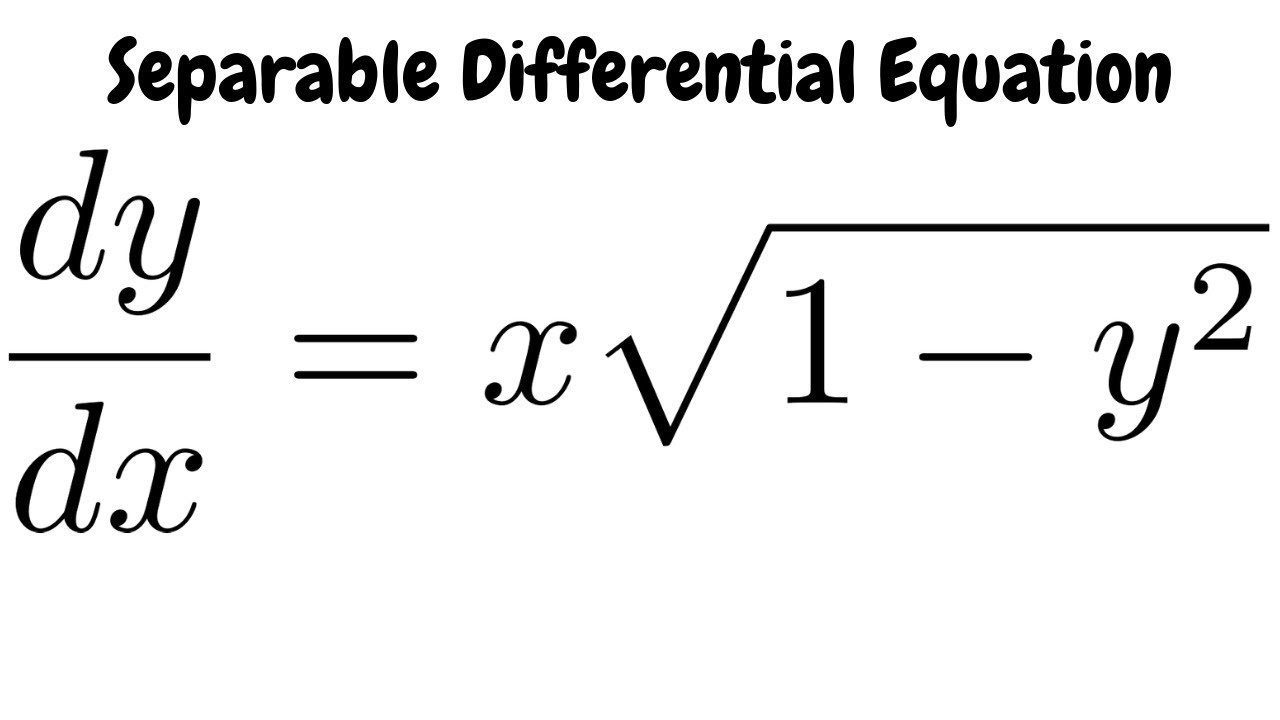


Separable Differential Equation Dy Dx X Sqrt 1 Y 2 Youtube



Form Differential Equation 1 Y 2 1 Log X Dx Xdy 0 Given Y 1 When X 1



The Solution Of The Differential Equation 1 Y X 2y Dx X
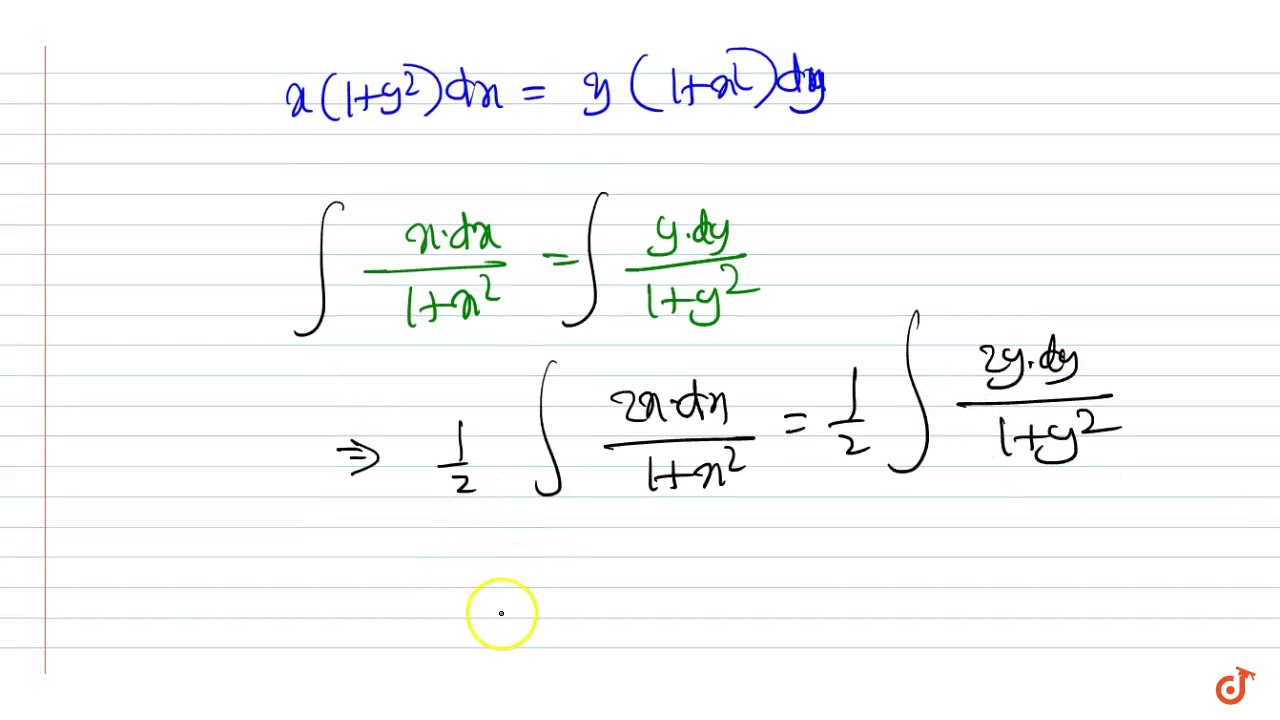


X 1 Y 2 Dx Y 1 X 2 Dy 0 Youtube
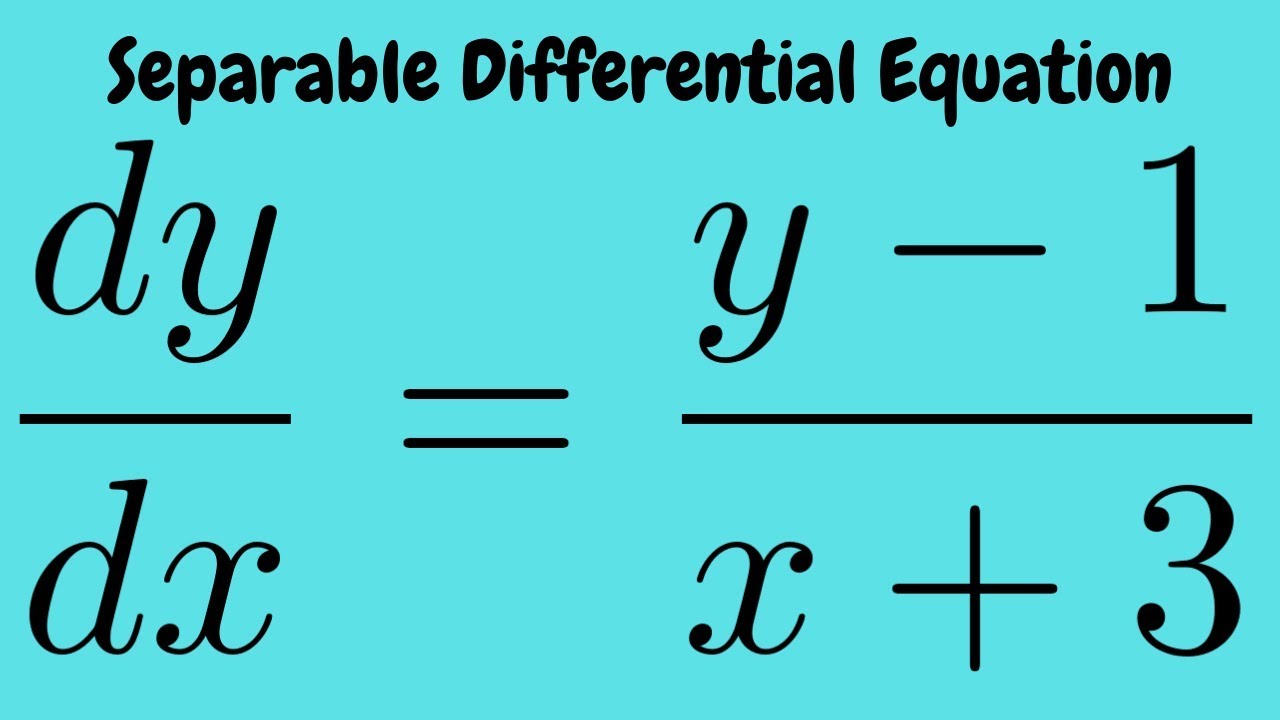


Initial Value Problem Dy Dx Y 1 X 3 With Y 1 0 Separable Differential Equation Youtube



If Y X Sqrt 1 X 2 N Then 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 X Dy Dx



Solution Manual For Differential Equations An Introduction To Modern Methods And Applications 3rd Ed By Iencm7 Issuu



If Y X X Prove That D 2y Dx 2 1 Y Dy Dx 2 Y X 0 Brainly In



If Y Sin 1 X 1 X2 1 2 Show That 1 X2 D2y Dx2 3x Dy Dx Y 0 Explain In Great Detail Mathematics Topperlearning Com Wa3tv55



Math 432 Hw 2 5 Solutions Pdf Free Download



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿